Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Model 1 - Reading GeoTop Data¶
This tutorial demonstrates how to read borehole data using GeoTop and set up the stratigraphic pile using GemPy.
Step 1: Import Necessary Libraries
Here we import the libraries necessary for handling the environment variables, numerical operations, data handling with pandas, and the specific functions from subsurface and gempy packages.
import dotenv
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import subsurface
import gempy as gp
from gempy_geotop.model_constructor import initialize_geomodel, add_fault_from_unstructured_data
from gempy_geotop.geotop_stratigraphy import stratigraphy_pile, color_elements
from gempy_geotop.reader import read_all_boreholes_data_to_df, read_all_fault_data_to_mesh, add_raw_faults_to_mesh
from gempy_geotop.utils import plot_geotop
Step 2: Load Environment Variables
Environment variables are a secure way to manage configurations and sensitive data. Here we load the environment variables that specify the path to the borehole data.
dotenv.load_dotenv()
True
Step 3: Read Borehole Data
We read the borehole data from the specified directory. This data will be used to initialize and configure the geological model in GemPy.
data_south: pd.DataFrame = read_all_boreholes_data_to_df(
path=os.getenv('BOREHOLES_SOUTH_FOLDER')
)
Step 4: Initialize GemPy Model
Using the borehole data, we initialize the GemPy model. We also slice the formations to consider only the first 10, adjusting the model’s complexity and processing time.
geo_model = initialize_geomodel(data_south)
slice_formations = slice(0, 10) # Slice the formations to the first 10
depth = -500.0 # Define a fixed depth for the model's base
[120071, 209998, 370060, 419970, -901.5, 48.68]
Step 5: Map Stratigraphy and Color Elements
Here we map the stratigraphy pile to the GemPy model and assign colors to different geological units for better visualization.
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces(
gempy_model=geo_model,
mapping_object=stratigraphy_pile
)
color_elements(geo_model.structural_frame.structural_elements)
Could not find element 'VE' in any group.
Could not find element 'RU' in any group.
Could not find element 'TO' in any group.
Could not find element 'DO' in any group.
Could not find element 'LA' in any group.
Could not find element 'HT' in any group.
Could not find element 'HO' in any group.
Could not find element 'MT' in any group.
Could not find element 'GU' in any group.
Could not find element 'VA' in any group.
Could not find element 'AK' in any group.
Step 6: Configure and Set Grid
We set up the grid for the model, defining its spatial extent and resolution based on the surface points and a specified depth.
geo_model.structural_frame.structural_groups = geo_model.structural_frame.structural_groups[slice_formations]
xyz = geo_model.surface_points_copy.xyz
extent = [
xyz[:, 0].min(), xyz[:, 0].max(),
xyz[:, 1].min(), xyz[:, 1].max(),
depth, xyz[:, 2].max()
]
geo_model.grid.regular_grid.set_regular_grid(
extent=extent,
resolution=np.array([50, 50, 50])
)
array([[ 1.2097027e+05, 3.7055910e+05, -4.9451320e+02],
[ 1.2097027e+05, 3.7055910e+05, -4.8353960e+02],
[ 1.2097027e+05, 3.7055910e+05, -4.7256600e+02],
...,
[ 2.0909873e+05, 4.1947090e+05, 2.1246000e+01],
[ 2.0909873e+05, 4.1947090e+05, 3.2219600e+01],
[ 2.0909873e+05, 4.1947090e+05, 4.3193200e+01]])
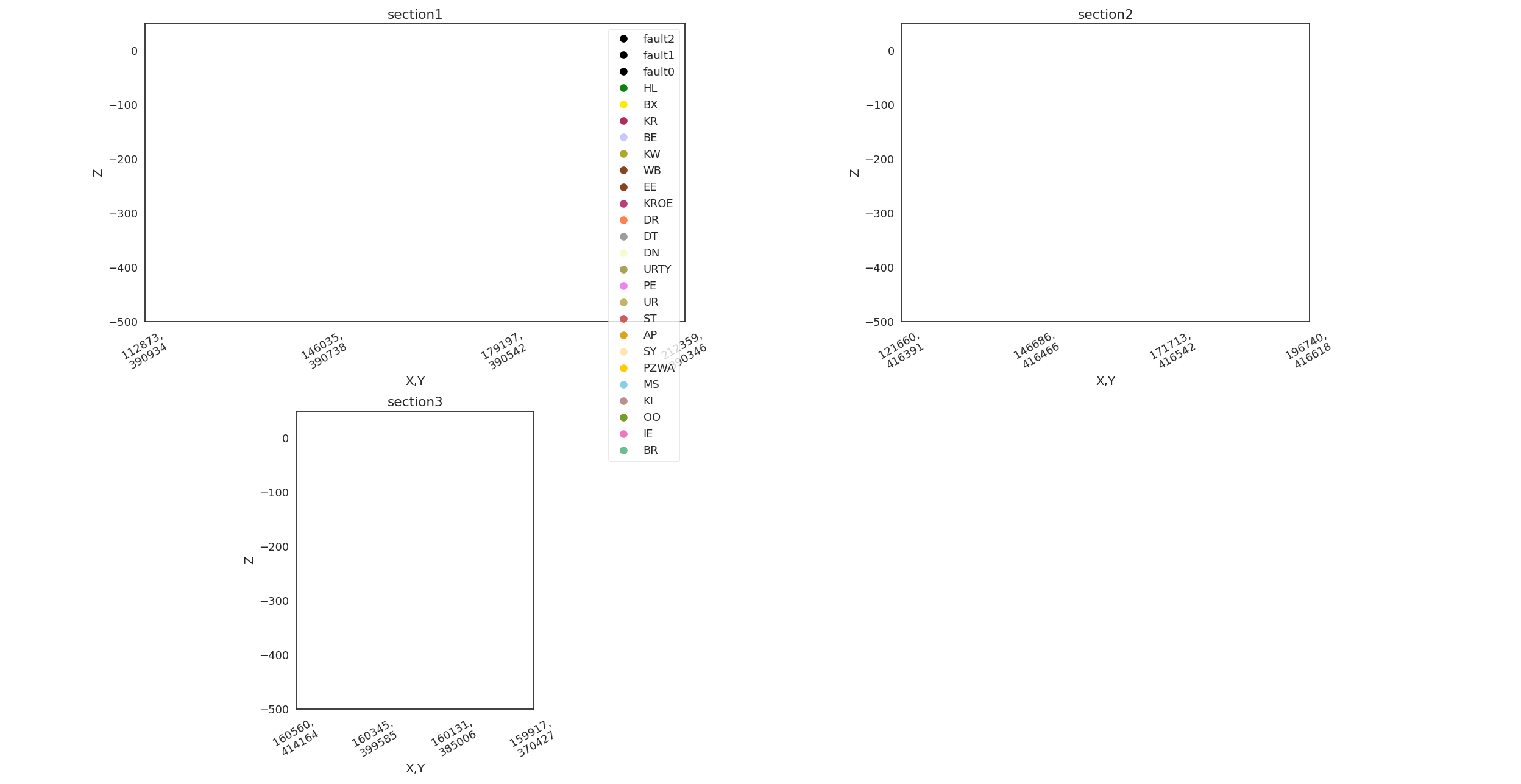
Step 7: Set Sections for Visualization
We define specific sections of the model for detailed visualization. These sections help in analyzing the model from different perspectives and depths.
gp.set_section_grid(
grid=geo_model.grid,
section_dict={
'section1': ([112873, 390934], [212359, 390346], [100, 100]),
'section2': ([121660, 416391], [196740, 416618], [100, 100]),
'section3': ([160560, 414164], [159917, 370427], [100, 100])
}
)
Active grids: ['sections']
Step 8: Read and Process Fault Data
We read fault data, slice it for processing the first few entries, and integrate these faults into the geological model.
all_unstruct: list[subsurface.UnstructuredData] = read_all_fault_data_to_mesh(
path=os.getenv('FAULTS_SOUTH_FOLDER')
)
slice_faults = slice(0, 3) # Slice the faults to the first 3 for simplicity
subset = all_unstruct[slice_faults] # Take the first 3 faults
for e, struct in enumerate(subset):
add_fault_from_unstructured_data(
unstruct=struct,
geo_model=geo_model,
name=f"fault{e}"
)
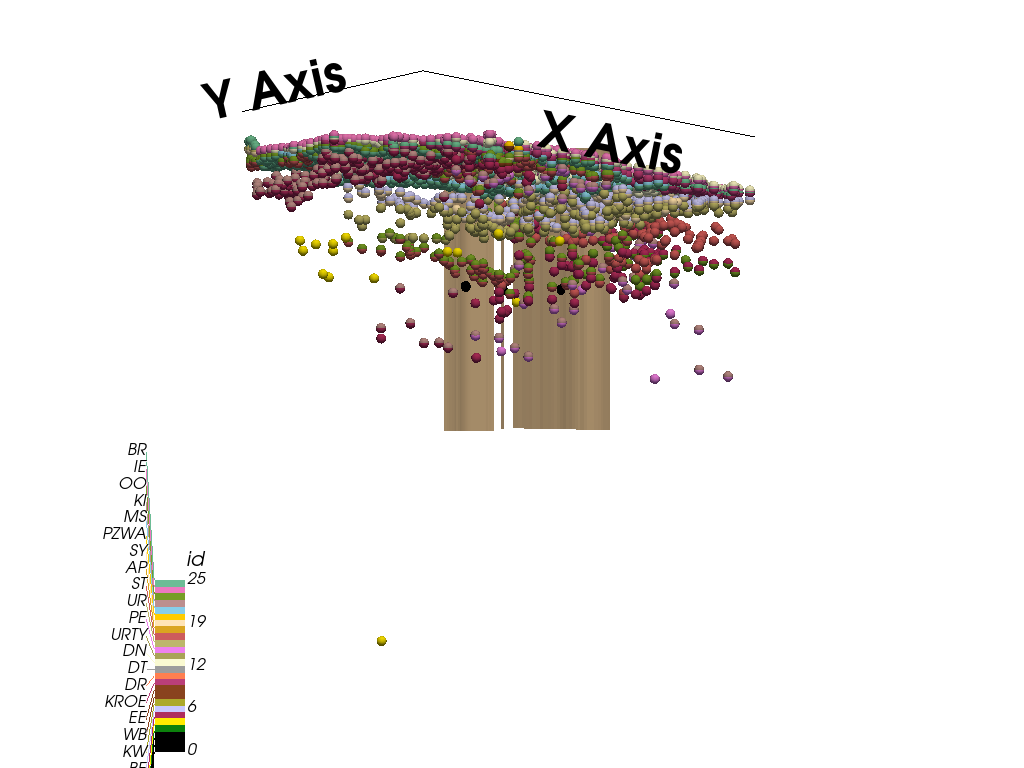
Step 9: Visualize the Model
Finally, we plot the 3D visualization of the geological model, showing both the stratigraphy and the faults. Adjust the vertical exaggeration for better depth perception.
plot_3d = plot_geotop(geo_model, ve=100, image_3d=False, show=False)
add_raw_faults_to_mesh(subset, plot_3d)
plot_3d.p.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.776 seconds)