Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
1.3b: 2-D sections¶
Importing
import gempy as gp
import gempy_viewer as gpv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
np.random.seed(1234)
Setup the model¶
Importing the data from CSV-files and setting extent and resolution
data_path = 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cgre-aachen/gempy_data/master/'
geo_model: gp.data.GeoModel = gp.create_geomodel(
project_name='Tutorial_ch1_1_Basics',
extent=[0, 2000, 0, 2000, 0, 750],
resolution=[20, 20, 20], # * Here we define the resolution of the voxels
refinement=4, # * Here we define the number of octree levels. If octree levels are defined, the resolution is ignored.
importer_helper=gp.data.ImporterHelper(
path_to_orientations=data_path + "/data/input_data/getting_started/simple_fault_model_orientations.csv",
path_to_surface_points=data_path + "/data/input_data/getting_started/simple_fault_model_points.csv",
hash_surface_points="4cdd54cd510cf345a583610585f2206a2936a05faaae05595b61febfc0191563",
hash_orientations="7ba1de060fc8df668d411d0207a326bc94a6cdca9f5fe2ed511fd4db6b3f3526"
)
)
gp.map_stack_to_surfaces(
gempy_model=geo_model,
mapping_object= # TODO: This mapping I do not like it too much. We should be able to do it passing the data objects directly
{
"Fault_Series": 'Main_Fault',
"Strat_Series": ('Sandstone_2', 'Siltstone', 'Shale', 'Sandstone_1')
}
)
gp.set_is_fault(
frame=geo_model.structural_frame,
fault_groups=['Fault_Series']
)
Surface points hash: 4cdd54cd510cf345a583610585f2206a2936a05faaae05595b61febfc0191563
Orientations hash: 7ba1de060fc8df668d411d0207a326bc94a6cdca9f5fe2ed511fd4db6b3f3526
Add sections¶
pass section dictionary with startpoint, endpoint and resolution for every section:
gp.set_section_grid(
grid=geo_model.grid,
section_dict={
'section1': ([0, 0], [2000, 2000], [100, 80]),
'section2': ([800, 0], [800, 2000], [150, 100]),
'section3': ([0, 200], [1500, 500], [200, 150])
} # p1,p2,resolution
)
Active grids: ['sections']
Add topography¶
gp.set_topography_from_random(
grid=geo_model.grid,
fractal_dimension=1.2,
d_z=np.array([300, 750]),
topography_resolution=np.array([50, 50])
)
Active grids: ['topography' 'sections']
<gempy.core.data.grid_modules.topography.Topography object at 0x7f088aa12350>
Active grids:
array([False, False, True, True, False])
gpv.plot_section_traces(geo_model)
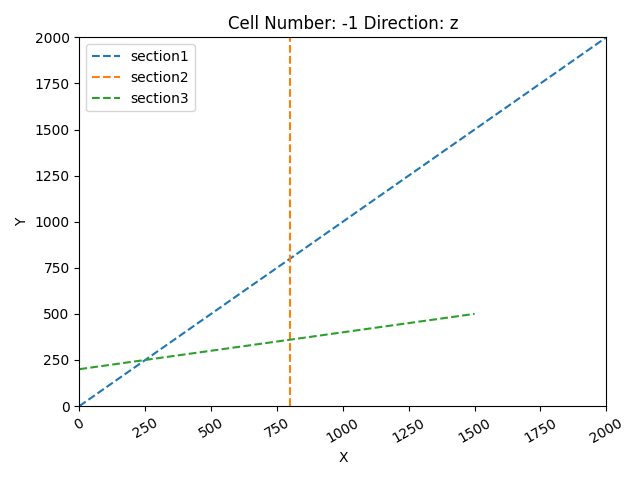
<function plot_section_traces at 0x7f08fe6e30a0>
geo_model.interpolation_options.mesh_extraction = False
sol = gp.compute_model(geo_model)
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.numpy
/home/leguark/gempy/gempy/core/data/geo_model.py:164: UserWarning: You are using refinement and passing a regular grid. The resolution of the regular grid will be overwritten
warnings.warn(
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, section_names=['topography'])
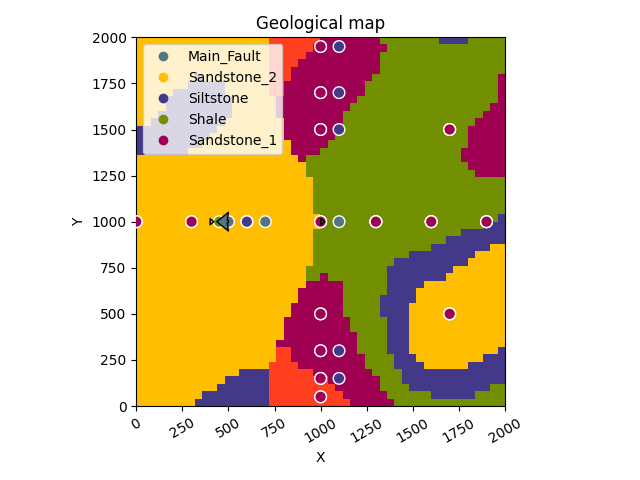
/home/leguark/gempy_viewer/gempy_viewer/API/_plot_2d_sections_api.py:106: UserWarning: Section contacts not implemented yet. We need to pass scalar field for the sections grid
warnings.warn(
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7f08f21b9330>
gpv.plot_2d(geo_model, section_names=['section1'])
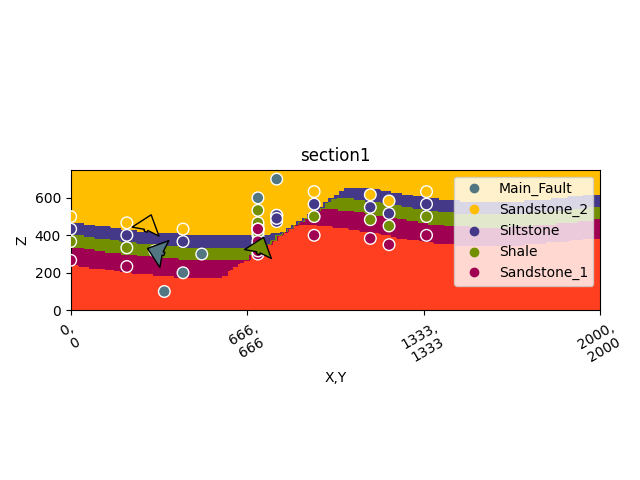
/home/leguark/gempy_viewer/gempy_viewer/API/_plot_2d_sections_api.py:106: UserWarning: Section contacts not implemented yet. We need to pass scalar field for the sections grid
warnings.warn(
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7f08f21bb220>
gpv.plot_2d(
model=geo_model,
section_names=['section1', 'section2', 'section3', 'topography'],
show_topography=True
)
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 4
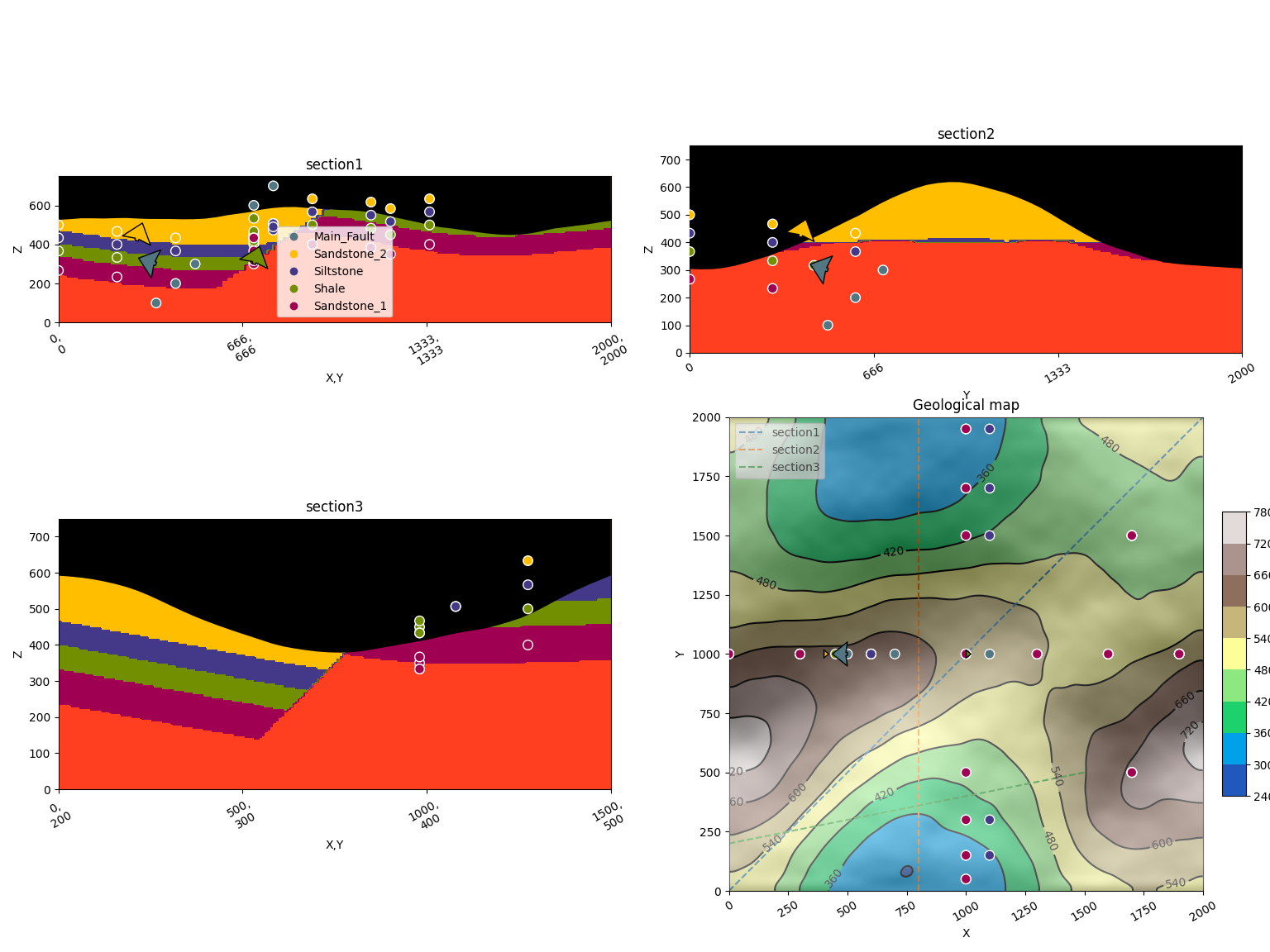
/home/leguark/gempy_viewer/gempy_viewer/API/_plot_2d_sections_api.py:106: UserWarning: Section contacts not implemented yet. We need to pass scalar field for the sections grid
warnings.warn(
/home/leguark/gempy_viewer/gempy_viewer/API/_plot_2d_sections_api.py:106: UserWarning: Section contacts not implemented yet. We need to pass scalar field for the sections grid
warnings.warn(
<gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D object at 0x7f08f51b72b0>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.974 seconds)
